Metaverse related news is coming in at a rapid pace these days. The metaverse has become such an important issue that news sources seldom stop to fully explain what it is and why it’s so important. This metaverse world can seem complex. Metamandrill continuously explores, experience, and discuss the metaverse, underlying technologies, and related subjects. Within this metaverse guide, we aim to turn our knowledge into clear information, so that you can join us on our journey to the future where the online and physical world merges.
Quick Menu Metaverse Guide:
- The Metaverse Explained
- What Are Characteristics of The Metaverse?
- The 7 Layers of The Metaverse
- 1. An Experience of Dismaterialized Reality
- 2. Discovery and Exploration of a Vast and Living World
- 3. An Economy Where Creators Can Thrive
- 4. Spacial Computing That Blurs Boundaries Between the Real and Virtual Worlds
- 5. A Decentralized Experience With Interoperable Components
- 6. Human Interfaces Which Allow for Direct Interaction
- 7. An Infrastructure That Creates the Larger Virtual Network and Interfaces
- Extended Reality & Its Components
- Examples of Companies Developing The Metaverse
- Contrasting and Comparing the Metaverse to Web 3.0
- Early Versions of The Metaverse
- 5 Examples of Today & Future Applications of The Metaverse
- With Which Devices Can You Enter The Metaverse?
The Metaverse Explained
Let’s start the Metaverse guide by explaining what the metaverse actually is. The metaverse meaning is flexible and can describe different experiences. The metaverse can be an entire virtual world that you’re immersed in via a VR headset. But the metaverse can also integrate itself into the world around you through a more mobile digital overlay. This augmented reality-based approach recently gained widespread recognition through Pokémon GO.
It’s essential to keep in mind that the metaverse has emergent properties. It allows for collaboration, even merging, of online and offline components. This opens up the prospect of continual growth and development. The metaverse is essentially a new digital universe that exists alongside our own. But it’s a universe that can merge with our own to create immersive, interactive, and hyper-realistic experiences.
The metaverse is still in development and can be thought of as an amazing experiment that’s constantly creating new surprises. Different companies and developers can create dramatically different takes on the concept. Nobody knows exactly what the metaverse will look like in the future. But you can jump into it today and see that growth firsthand.
What Are Characteristics of The Metaverse?
Within this part of the metaverse guide, you are going to learn about the characteristics of the metaverse. The metaverse is in continual development. As such, people can always expect to find new features and surprises when they log in. But there are a few features that are consistent across all implementations of the metaverse. Different implementations might indeed work with these rules in different ways. However, for the most part, you can rely on these central points within any variation on the metaverse.
There Are No Limits or Boundaries
The metaverse is essential without limits or boundaries. You might find areas that you can’t move beyond. But this is simply because nothing has been built within those areas yet. The space is essentially endless. It merely needs to be properly utilized by the metaverse-centered programmers.
No Singular Authority Is in Control
The metaverse isn’t like a single home or building that one person owns. It’s instead more like a large area of land where many different people live. In the physical world, people have deeds and proof of ownership. In the metaverse, people often demonstrate it through blockchain-related systems.
It’s Always Active and Can’t Be Turned Off
Nobody can turn off the earth. Likewise, people can’t turn off the metaverse. It’s a decentralized system that’s made up of many independent parts. True, some elements of the metaverse might only exist on a single server that might go offline. But the metaverse itself isn’t on a single server.
It Has a Functional Economy Similar to the Real World
You can expect a functional economy in the metaverse powered by cryptocurrency. People will use it to buy virtual land or goods similar to the real world. Digital assets which use art are typically protected as NFTs. All this makes it possible to buy and sell.
It Provides an Immersive Sensory Experience
The metaverse fully engages one or more senses. This is typically vision, through VR goggles. And of course, audio cues come in through headphones. But the metaverse has the potential to immerse people through any of their various senses fully. This immersion also entails letting users modify their virtual environment.
People Can Make Real Social Connections
The metaverse lets people make real social connections. These experiences typically happen with other human beings. But even interactions with AI can provide social stimulation. Social interaction means people are always surprised and can find new experiences by talking to others. This also leads to exploration and the metaverse’s economy.
The 7 Layers of The Metaverse
Within this part of the metaverse guide, you are going to learn about the 7 laters of the Metaverse. It’s helpful to think of the metaverse in terms of layers surrounding its users. People need to keep in mind that there’s no particular order to these layers. But as people enter into or enhance these layers they become more connected to the metaverse. In a sense, they’re more fully citizens of the metaverse as they gain strength or presence in each layer. The 7 layers are suggested by Jon Radoff, author of Building the Metaverse blog.
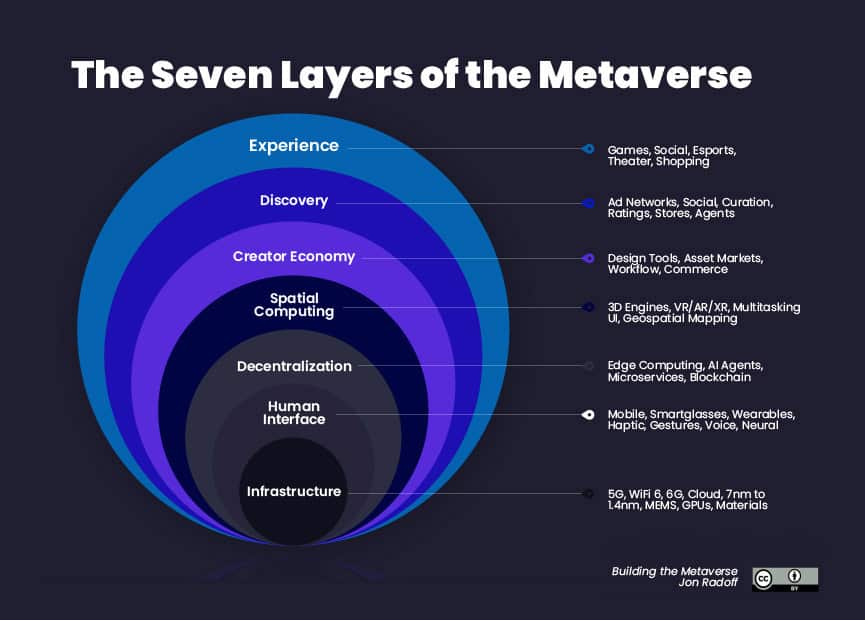
Image attribution: “The 7 Layers of The Metaverse”, by Jon Radoff, licensed under CC BY 2.0
1. An Experience of Dismaterialized Reality
People often visualize the metaverse as a 3D space. And it’s true, users generally interact with the metaverse in that way. For example, VR goggles simulate 3D environments. Interface devices make it possible for users to grip or move items in those 3D environments. However, the metaverse isn’t a 3D space. It’s not a 2D space either.
The metaverse is instead a dematerialized reality where spatial dimensions are irrelevant. For example, Alexa exists within small objects that connect to massive amounts of information. And people within the metaverse can explore vast amounts of virtual land that ultimately exists as something as small as a hard drive.
The metaverse essentially dissolves people’s concept of spatial dimensions. And this isn’t just within the metaverse itself. The internet of things (IoT) can bring the metaverse into the real world just as people can find elements of the real world inside the metaverse.
2. Discovery and Exploration of a Vast and Living World
Exploration of the metaverse is a vital layer that’s not always easy to understand. Exploration doesn’t just involve looking through a simulated 3D environment. Of course, this type of exploration is part of the more extensive experience of the metaverse. Many people love the chance to be among the first to see new sights within the continually expanding landscapes of the metaverse.
However, as previously noted, there’s more to the metaverse than 3D environments. Discovery and exploration also involve inbound discoveries. For example, community-created content will often find its way to users. And there will usually be commercial interests looking for people who have specific and compatible interests.
Discovery within the metaverse can also be outbound. For example, advertisements or what most people think spam would be considered outbound discovery. But all of these examples have something in common. They all highlight people finding new experiences in the metaverse.
3. An Economy Where Creators Can Thrive
The metaverse has a whole economy. As previously noted the metaverse tends to rely on blockchain-based exchanges based on cryptocurrency. But the metaverse’s economy goes beyond the simple exchange of currency for goods and services. A creator economy sets the metaverse’s economy apart from the real world.
Both the early web and metaverse went through two initial points of development. The first is the pioneer era. This period required people to have a high level of expertise to create content in the digital realm. For example, one would have to be an expert programmer to create content for the early internet or metaverse. Next came the engineering era, where new tools make it easy for even new developers to create content.
But what makes a true metaverse is the creator era. Here average users can create goods. Likewise, they can easily sell goods too.
4. Spacial Computing That Blurs Boundaries Between the Real and Virtual Worlds
As previously noted, the metaverse tends to erase the limits of spatial dimensions. As the metaverse develops, it essentially blurs the digital and analog worlds. What’s virtual and what’s real? It’s easy to say that the digital realm isn’t real. But when you have your money, unique purchases, and even property online? That becomes very real. Likewise, a room devoted to VR might have very little to do with that location’s physicality.
Meanwhile, the digital realms can simulate 3D spaces. You can go on walks along virtual trails and see real effects. You’ll traverse virtual distances, burn calories as you move your legs or arms, and even feel relaxed watching distant horizons.
In a sense, you’re not traveling a significant distance as measured in analog terms. You might simply be walking in place or along a small track. But what matters is the feeling.
5. A Decentralized Experience With Interoperable Components
Centralized computing consists of a single entity or component which controls an entirely digital system. This is the easiest way to design or use networks. However, it doesn’t provide much freedom or power to end-users. The metaverse instead relies on decentralized development. This means that the metaverse consists of many individually owned and created components.
The exact nature of decentralization varies between implementations. However, one crucial point shared between all aspects of the metaverse is interoperability. People create elements based on standards, making them interoperable with each other. This means components can be essentially removed and replaced. This is similar to eliminating RAM from a computer and replacing it with a RAM stick from another manufacturer.
The metaverse uses shared standards to work with things like the blockchain. But it also means that people can write their extensions or apps.
6. Human Interfaces Which Allow for Direct Interaction
People often don’t realize just how much they interact with technology. For example, a smartphone is less a phone and more of a supercomputer with a powerful network behind it. These devices also have various sensors and even some limited AI to further aid interaction. And almost everyone interacts with it throughout the day without giving it much thought.
Smartphones aren’t just getting smaller and easier to use. They’re also being integrated into interface devices for the metaverse. For example, the Oculus Quest is essentially a combination of VR and smartphones. The process of integrating components effectively creates a human interface into the metaverse. People are, in large part, becoming cyborgs.
The internet of things is making everyday household items smarter. Items such as smart glasses bring a range of new capabilities. The trend of adding new sensors to people’s bodies is expected to continue.
7. An Infrastructure That Creates the Larger Virtual Network and Interfaces
Finally, the metaverse depends on a complex infrastructure. People often think of this as a nebulous system. However, the metaverse’s components are usually fairly familiar to most people. For example, everyone’s familiar with wireless networks thanks to the constant use of their phones. 5G networks aren’t just going to improve the quality of calls. It also offers better data speeds. This means that people’s ability to access the data-rich metaverse will also increase.
The increased capability of mobile devices makes for a better interface. But it also means that it’s easier to construct VR and other display devices in compact form factors. The Oculus Quest shows that manufacturers can create systems that combine mobile components with VR tech.
The large-scale convergence of features between different technologies helps to further the development of the metaverse’s infrastructure. Increased development means more widespread access to the metaverse.
Extended Reality & Its Components
The metaverse as a whole should be seen as a single unified concept bound by an underlying meaning. Accessing the metaverse creates an extended reality simply due to the fact that it necessitates a blending of the physical and virtual space. But this can be accomplished in different ways. And as you’ll soon see, each technology used to access the metaverse creates a distinct form of extended reality.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality is a form of extended reality that essentially overlays the metaverse onto the physical world. This can manifest in relatively subtle ways. For example, you might see an arrow pointing the way to your destination if you’re using an AR-based map app. But advanced AR systems can even introduce new elements or informational overlays above specific physical items. Imagine walking through a museum and seeing pop-up text describing a piece’s relevant history.
You can look into augmented reality’s past, present, and future in the article “Augmented Reality; Learn About AR Tech, Use Cases, Devices, and More!”.
Mixed Reality
Mixed reality can be thought of as a more advanced form of augmented reality. The major difference between the two comes from the level of integration between the metaverse and physical world. Augmented reality tends to have a lower level of potential interaction between digital and physical elements. Mixed reality provides more options for physical actions to register with digital entities. For example, MR entities might walk around an obstacle such as a chair instead of moving through it.
You can delve into the larger story of mixed reality in the article “Mixed Reality; Everything to Know About MR Technologies”.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality is what most people think of when discussing the metaverse. Users don a VR headset that encompasses their full range of vision with digital displays. The headset also tracks the user’s specific head motion. Some VR headsets even track eye movement. All of these elements and more are processed by the system’s software to simulate interaction with a virtual world. For example, turning your head in the physical world moves your view in the virtual.
You can learn about the components, history, and use of VR in the article “Virtual Reality; Discover VR, Its Components, Technology, and Players”.
Examples of Companies Developing The Metaverse
Within this part of the metaverse guide, you’ll find examples of companies who are for a big part responsible for developing the metaverse. The metaverse is in large part a collaborative project. Individuals and larger companies contribute their skills and resources to make sure the metaverse continues to grow. But some companies stand apart from the rest with their contributions. The following companies have added some significant things to the internet.
Meta (Previously Facebook)
Facebook showed its dedication to the metaverse when it rebranded into Meta. The company is responsible for one of the most popular VR devices – Oculus. They also have a more expensive cutting-edge platform in Cambria. Meta is also investing in the software side of the metaverse.
The Horizon Marketplace gives users a virtual area to buy and sell goods. Meanwhile, the company is also working on various programming APIs to develop their apps or code for the metaverse. This dual approach of hardware and software makes them a key player.
For more information about Facebook and the metaverse, read “Facebook Metaverse; Explained, Examples, Devices, Vision & Critics”.
Video: Facebook Horizon
Microsoft
Microsoft is mainly notable for its work on Mesh for Teams. Microsoft took notice of just how many people had started to work from home during the pandemic. With the increased interest in the Metaverse, it was clear that they could create something for that audience. The result is a system that lets people use avatars within a persistent virtual office.
The system is also compatible with both common and more advanced hardware setups. This means that if people have VR equipment, they can get the most out of Mesh for Teams. But people can use standard equipment too.
Video: Introducing Microsoft Mesh
Bytedance
Bytedance is tackling the difficult balance of economics within the metaverse. Setting up a system for buying and selling items is one thing. But it’s quite another to fully stabilize an interoperable experience that can persist between different metaversal implementations. Bytedance is making this a reality through blockchain development and token pairs.
Their system also supports Metaverse tokens to simplify things for users. This is coming together to help create stable systems, like the Binance NFT Marketplace, where people can engage in financial transactions. The focus on compatibility between systems will also encourage its growth.
Sony (Epic Games)
Sony, with Epic Games, is one of the biggest players in the metaverse. However, many people don’t realize it until that fact is pointed out. That’s because their contribution to the metaverse started as a simple game – Fortnite. Fortnite might have begun as just a game. But it’s grown into a major platform where people can play, socialize, and even attend virtual performances.
It currently has over 60 million monthly users. And it’s expected that the userbase will continue to grow as they introduce new 3D, AR, and VR content into it.
Video: Your World is Endless in Fortnite Creative Trailer
Roblox
One of the company’s most notable contributions to the metaverse comes from continuing to build upon one of their most popular games – Roblox. Roblox refers to both a particular company and one of the company’s most popular video games. The game offers players a chance to create and enjoy content with other players.
This has culminated in some awe-inspiring collaborative efforts over the years. And the company keeps adding new features into the mix. One of the most recent additions for players is a spatial voice chat which helps to make the environment feel more authentically sociable.
Video: Roblox Cinematic
Niantic
Niantic is perhaps best known for its smash-hit Pokémon GO. The game combines the popular Pokémon franchise with augmented reality to create a magical metaverse experience. People were enthralled by interacting with Pokémon characters in the real world. But the company hasn’t stopped there. Niantic has raised over $300 million for future work on the metaverse.
Given that Niantic was many people’s first introduction to augmented reality and the metaverse it’s clear that they already have a built-in audience. Founder and CEO John Hanke commented on his future plans. He wants to create “reality made better”.
Video: Niantic – Meet You Out There
Nvidia
Nvidia is one of the most well-known names among anyone interested in digital design. Their GPUs power a huge chunk of the machines working with 3D graphics. And now Nvidia is using its position to help encourage the development of the metaverse. The company is giving away a free version of its “Omniverse” software to individual artists.
Putting professional-level software out there should encourage new content. This software suite gives designers the ability to craft full virtual worlds and assets. Users will also be able to take their creations online into their choice of digital marketplaces or content libraries.
Video: VIDIA Omniverse and a Future of Shared Worlds
Decentraland
Decentraland is one of the leaders in fully established metaversal implementations. It offers a full world where people can explore and socialize. But at the moment it’s perhaps best known for the high-priced financial transactions which take place within it. A large patch of land within the Decentraland system recently sold for $2.4 million in cryptocurrency.
The large price is noteworthy. It highlights that Decentraland has a well-established economy with NFTs, land deals, and other essential functions. But what’s equally important is the simple fact that people can easily make transactions like that.
Video: Decentraland Avatars
Google was one of the early pioneers in AR with its Google Glass platform. Google Glass didn’t move into the public space like most people assumed it would. However, the company has had success with it in the private sector. In late 2021 Google merged and reorganized their VR and AR departments into a new team under their Google Labs moniker.
This team is now working on a holographic video conferencing system called Project Starline. They’re preparing for further investigation into both AR and the metaverse. They probably have a lot more in the works.
Video: Google Project Starline: Feel like you’re there, together
Tencent
Tencent has been around since 1998. During that time it’s extended into most areas involving digital development. They’re perhaps best known for their TiMi Studio Group. This development studio has created some of the world’s best-known video games. At the moment, it’s not known precisely how Tencent will leverage that success into the metaverse. But their technical systems have already mirrored many of the essential parts of the metaverse. It’s thought that the company’s “multiverse platform” will launch as a direct competitor to Meta. The specifics of Tencent’s take on the metaverse are currently unknown but will undoubtedly impress.
Contrasting and Comparing the Metaverse to Web 3.0
Anyone familiar with Web 3.0 might notice many similarities to the metaverse. There’s a good reason for that fact. Web 3.0 can be thought of as implementing the metaverse built on top of the internet. You use a web browser to access metaversal content rather than a VR headset or augmented reality glasses.
For example, consider how many of the previous examples of companies and implementations of the metaverse use NFTs, cryptocurrency, and the blockchain. These economic currencies and goods are tied to the metaverse. But at the same time, you can also use them through standard web browsers.
However, this is just one example of a multitude of possibilities. Web 3.0 could connect people with AI systems encountered in the metaverse. Or users might decide to look through summaries of real estate listings found in the metaverse.
Early Versions of The Metaverse
There have been earlier versions of the metaverse. One of the best early metaverse examples is Second Life, which is still running today. At the service’s peak, it had around 900,000 active users. Second Life is still one of the best examples of the concept since users can create their worlds and avatars.
Collaborative social games like Roblox, Fortnite and even some MMOs can also be thought of as prototypical forms of the metaverse. However, these experiences don’t provide users with the full range of immersion you’ll find in the modern metaverse implementations.
5 Examples of Today & Future Applications of The Metaverse
Within this part of the metaverse guide, you’ll find examples of applications that are developed for the metaverse. The metaverse’s presence might seem pretty new. But we can already find examples of it almost everywhere. It’s entered into almost every aspect of life. And this ranges from gaming to entertainment and even a wide variety of business options.
1. Virtual Worlds
A virtual world is a computer-simulated environment that may be visited by multiple users simultaneously or independently, each of whom can create an individual avatar and explore different virtual spaces, create their own spaces, engage in activities like events, and interact with others.
Horizon Worlds (from Meta – previously Facebook) is an example of a newly launched metaverse platform. Using the VR headset Oculus from Facebook people can create a personal avatar and wander around in an animated world, meet new people, join events and play games with others. Other examples of virtual worlds are Hubs Mozilla, Gather and Fortnite.
For more information about virtual metaverse worlds, read “Metaverse Virtual Worlds: The Best Way To Experience the Metaverse “.
Video: Getting Started with Mozilla Hubs Virtual Spaces
2. Gaming
In addition to Roblox, there’s a wealth of other gaming options. Decentraland, Axie Infinity, Sandbox, and Illuvium are some of the best metaverse options around. Arguably the most critical part of these platforms is immersion. Gaming presents a vibrant world where change isn’t just possible but also emphasized. Players have missions and motivations. And all of this takes place in a vivid social landscape that allows for deep connections. Taken as a whole, it feels like you’re living in an exciting and vibrant digital world. This also helps the environments attract new users to ramp up continually.
For more information about metaverse games, read “Top 10 Popular Metaverse Games To Explore Right Now”.
Video: Illuvium – Gameplay Reveal Trailer
3. Events
The metaverse has many events that mirror and even surpass what you’ll find in the real world. One of the metaverses, Sensorium Galaxy, is specially tailored to these types of amazing experiences. Artists like Armin van Buuren, Steve Aoki, David Guetta, and more are growing Sensorium Galaxy into something artistically breathtaking. It includes a whole world dedicated to music along with special places for meditation, fitness and similar practices.
Other services like Fortnite have paired with artists like Travis Scott and Ariana Grande. Fortnite is creating special interactive events tailored around artists in a unique Soundwave series. It’s hosted concerts by artists like Ariana Grande and Marshmallo. The American DJ set alone had over ten million in-game viewers. Fortnite even has events that highlight current trends in the real world. For example, JJ Abrams appeared as a usable custom avatar. Users were also treated to a new Star Wars clip within the game. This type of convergence between online and offline events is a hallmark of the metaverse.
Video: Fortnite x Ariana Grande
4. Corporate
Many people experienced online conferencing for the first time, thanks to COVID-19. This also demonstrated how limited webcams are. Some companies are already leveraging solutions based on their metaverses. Meta is leading the way with Horizon Workrooms. Microsoft has also created Mesh for Microsoft Teams. Mesh lets you add virtual metaversal flourish to remote meetings in Microsoft Teams. Most companies have seen just how valuable online engagement is. And employees love the freedom to work remotely occasionally. The metaverse is the next natural leap forward in that process. It can bring meetings and workplaces into fully immersive virtual worlds.
Video: Horizon Workrooms – Remote Collaboration Reimagined
5. Real Estate
$2.4 million might seem like a lot for some land. But that sale came through one of the metaverses popular hangouts – Decentraland. Other metaverses like Sandbox have seen similarly impressive transactions. Sometimes sales come through standard currency. Other times this might happen through cryptocurrency. But the fact is that metaverses tend to have thriving economies. This is hardly a new phenomenon either. Second Life, one of the programs that gave rise to the modern metaverse, had a flourishing virtual real estate scene in the early naughts. It even innovated digital economies with Linden Dollars.
Video: Decentraland – The virtual land selling for millions
With Which Devices Can You Enter The Metaverse?
Within this part of the metaverse guide, you’ll find an overview of devices that you can use to enter the metaverse. One of the largest differences between the early and modern versions of the metaverse is the equipment used to access it. Today’s powerful electronics can provide a truly immersive experience that makes it feel like you’re really in a different world. But which devices can you use to enter the metaverse?
Virtual Reality Headset (VR)
Virtual reality headsets sit over your eyes like a pair of high-tech goggles. Each of your eyes is presented with its digital display of the metaverse VR. The headset also keeps track of head positioning, so your view changes in the virtual world when you look around just as it would in the real world. Meta, formally known as Facebook, offers the Oculus Quest 2 headset. Meta also provides a relatively new app called Horizon Worlds for Facebook metaverse. Sony sells Playstation VR to gamers. And Microsoft metaverse option Hololens is the most expensive but also the most robust.
Augmented Reality (AR) Gear
Augmented reality gear is similar to VR gear in that both add digital images to our view of the world. The main difference is that VR entirely replaces our view of the world with a digital landscape. AR gear instead overlays digital elements to our view of the real world. AR gear essentially works with two different elements, which usually makes it more expensive. AR needs to be less bulky to allow you to wander around the world freely. It also needs to more carefully track your location since larger pieces of equipment don’t limit your movement.
Gaming Console
You might be surprised to find out that you already have the main component for the metaverse in your living room. The Xbox doesn’t have any VR or augmented reality support. However, it does provide platforms like Roblox and an interactive “metaverse museum”. If you have a Playstation, you can access VR features through its Playstation VR headset. Sony was an early innovator in metaversal concepts. Playstation Home offered cutting-edge innovations for the Playstation 3. You can expect similar leaps forward from Sony because PlayStation VR makes it such an appealing platform for metaverse development.
Computer
Computers are one of the best ways to access metaversal systems, thanks to their configurability. Computers are the most powerful option though not the most user-friendly. The majority of programs to access the metaverse run on PCs. However, it’s essential to keep in mind that not all computers are the same. A computer needs a good GPU (graphics processing unit) to render a virtual world’s geography. And of course, you’ll also need to buy a VR or AR system to use with your computer. You might even need to set up a crypto wallet for transactions within a metaversal system.
Mobile
Some metaverse apps like Axie Infinity are limited to a single mobile platform. But Roblox is available for Android, iOS, and many other platforms. Even your smartphone running iOS or Android can take you into a virtual world. Roblox even works on both platforms with and with VR support. This means that you can use the same platform on your phone as people with complex setups on dedicated home computers. Roblox is also a useful starting point because you can always upgrade your hardware while still working within the same software portal to your metaversal adventure.
For more information about VR and AR metaverse devices, read “Metaverse Devices: The Best Gear To Enter the Metaverse” .
Metaverses have a fantastic future and It’s equally clear that you can enjoy it today. Even modest equipment can give you a look into the metaverses. And more advanced technologies will let you see the most impressive innovations. We hope you enjoyed our Metaverse guide. If you have any suggestions or feedback, please leave a comment.
Did You Like This Article About The Metaverse?
You might also be interested in the following articles:
- Metaverse Trends; Upcoming Milestones for the Digital Frontier
- The Most Interesting Metaverse Blockchain Projects
- Metaverse Websites; The Best Way To Watch the Metaverse Grow
- Mark Zuckerberg Metaverse: The Full Story of a New Frontier
- Metaverse Avatar Guide; Embody Yourself in the Metaverse








I was looking for such a guide that you have written. Thank you. It well explains the metaverse.
Thank you for this metaverse guide; well explained!
What a good explanation of the metaverse. I like this article. Keep continuing the good work.