Augmented reality (AR) scanner technologies are progressing at a rapid pace, making this exciting technology ever more accessible to the average person. The scanners consist of a camera and additional sensors, usually optimized for artificial reality. The scanners bridge the physical and digital worlds by overlaying virtual information on top of physical items. Users will find themselves immersed in a uniquely interactive experience.
In this article, you’ll learn about the fundamental elements of AR scanners, their importance, how you can benefit from them, and how they will shape the future.
Table of Contents:
- What Are Augmented Reality Scanners and How They Work
- Core Components of Effective AR Scanners
- Types of Augmented Reality Scanners
- 5 Key Applications of AR Scanning Technology
- Top AR Scanner Apps in 2025
- Future Trends in Augmented Reality Scanners
- Augmented Reality Printing: How to Bring Static Content to Life?
- Augmented Reality Builder Options; Building Your Digital Dreams
- FAQs About Augmented Reality Scanners
What Are Augmented Reality Scanners and How They Work
Augmented reality scanner technologies differ on a case-by-case basis. However, an AR scanner will usually combine one or more cameras, sensors, and a program to process their input. There are options for standalone scanners, but they’re usually integrated into mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, industrial equipment, or smart glasses.
Like virtual reality (VR), AR lets people interact with digital, virtual elements. VR puts the user in a new virtual environment, while AR melds digital elements into the physical world to let you experience a unified whole. AR’s ability to seamlessly meld these two worlds makes it, and the scanners powering AR, an important tool for education, visualization, and real-world solutions.
Core Components of Effective AR Scanners
Judging any given augmented reality scanner requires looking at its individual components. The following elements form the foundation of most augmented reality scanning devices.
- Cameras and Sensors: The foundation of every augmented reality scanner will typically use multiple optical and sensory elements like motion trackers, depth sensors, and infrared sensors as data sources for further processing.
- Processing Hardware: Data from other elements are processed by a central processing unit (CPU), a graphics processing unit (GPU), or both for real-time operations.
- Recognition Software: Software leveraging computer vision algorithms to identify and categorize objects, movement, and other elements of physicality.
- Display Technology: The visual output of an AR scanner can range in complexity from a smartphone screen to a dedicated headset and enhances overall immersion.
- User Interface: The interface elements that enable users to control their AR experience, including detection and analysis, significantly impact the use of augmented reality scanner devices.
- Connectivity Options: Connections with networks and, through them, other devices give AR scanning technology the ability to offer updates, send or receive data, and work alongside other digital systems.

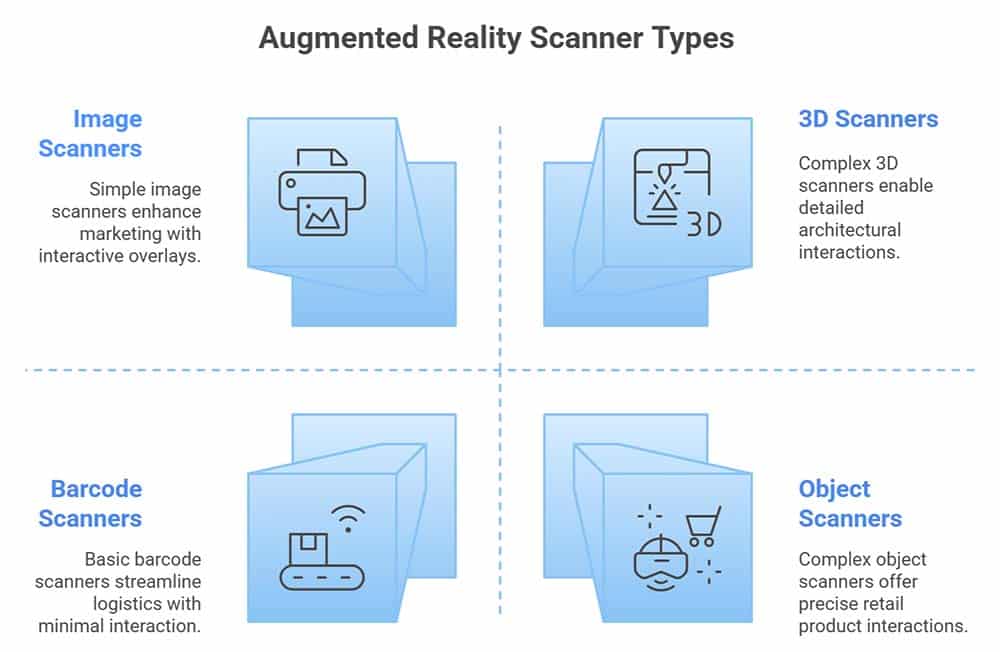
Types of Augmented Reality Scanners
Augmented reality scanner implementations are used for a variety of scenarios and are often designed to meet specific needs. The following are the most significant examples.
1. Augmented Reality Image Scanners
These AR camera scanners are used by pointing the lens at printed material. The AR system detects specific patterns and then overlays the corresponding AR data. Special algorithms are used to anchor these digital elements in place while users move around. The technique is especially popular for marketing campaigns. For example, users might scan a movie poster to see trailers spring to life in front of them. The technique bridges standard print marketing and immersive technology.
2. Augmented Reality Object Scanners
AR object scanners analyze physical 3D objects in an environment to create realistic interactions with digital elements. Spatial relationships between physical and digital elements, shapes, and even textures are handled by object scanners to ensure perfect alignment of the physical and digital world. It’s often used for scenarios where people depend on the exact positioning of objects in a physical environment. For example, retail AR empowers people to virtually try out products or see how furniture would look in their homes.
Video: AR Scanning and Detecting Objects Using ARkit iOS Object Tracking
3. Augmented Reality Barcode Scanners
AR scanner technologies can provide a significant boost over standard barcode scanners. A scanned barcode can be matched against continually updated information from the cloud to provide interactive elements alongside product information. These AR recognition systems are most popular in logistics and retail. Customers can instantly see everything from a product’s technical compatibilities with other items to nutritional information. In contrast, warehouse workers will see updated stock levels or other work-related information.
Video: Augmented Reality Burger on a Restaurant Menu via an AR QR Code
4. Augmented Reality 3D Scanners
An AR scanner can also move beyond single objects to model an entire physical environment through strategies like structured light analysis, photogrammetry, or LiDAR. Newly virtualized environments can then be further measured, modified, or enhanced by adding various digital information through AR. The technique is most common for tasks that require detailed representation of movement in 3D spaces, like architecture or game design. Game devs can scan environments for use in games, and architects can leverage a perfect real-world recreation of areas that need renovations.
5 Key Applications of AR Scanning Technology
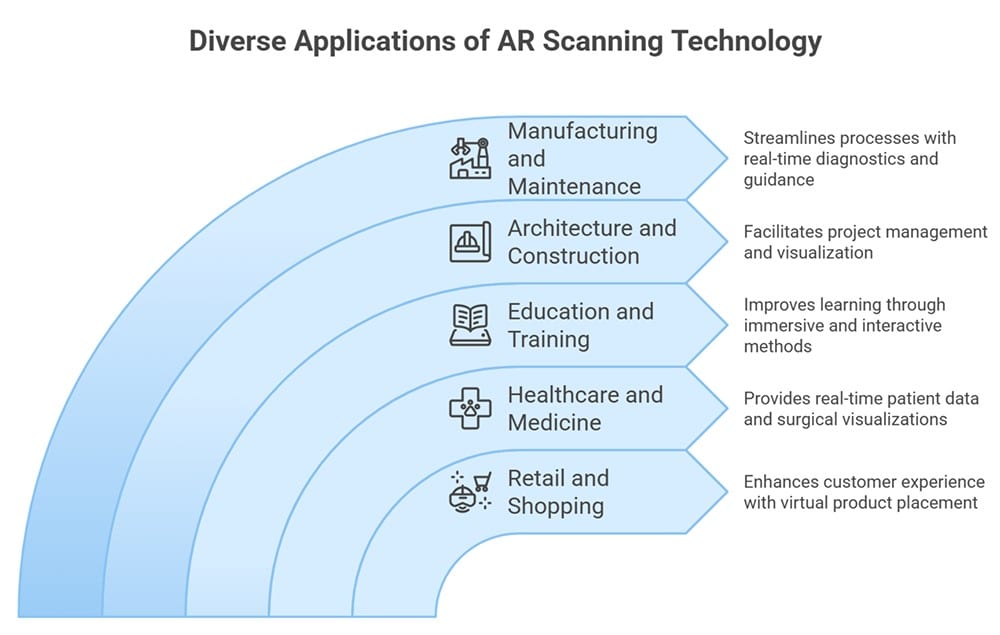
While AR scanner technologies are useful in almost every field, they’ve seen special success within the following sectors.
1. Retail and Shopping
Augmented reality scanner technologies let people directly experience how a product would fit into their lives. Users can simply point their phone at an area or person and see how clothing, furniture, and more would fit their needs. IKEA’s Place app, for example, makes it easy to virtually place digital recreations of IKEA furniture into their homes to see how it’d look. Or take Sephora’s Virtual Artist, which has shown a 28% increase in conversion rates by letting customers see how the makeup would look on them.
Video: Create 3D Scans & AR Codes on Any iPhone or iPad – No LiDAR Needed
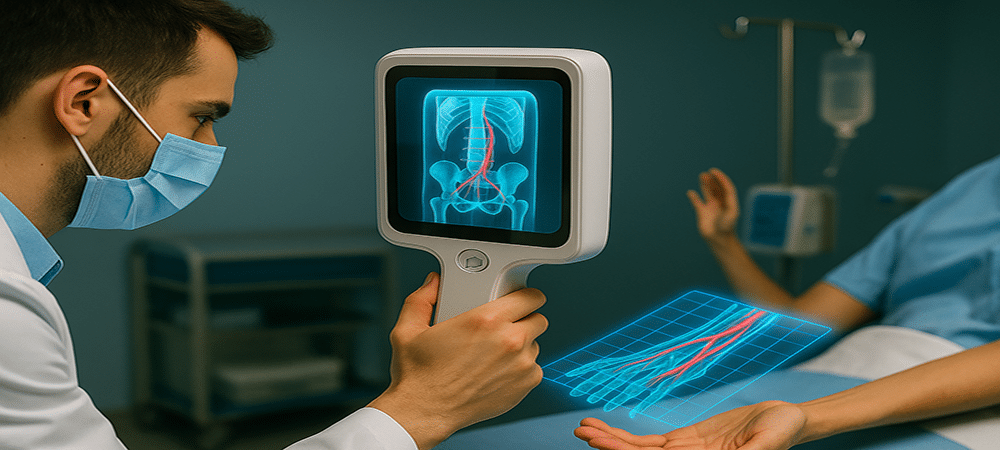
2. Healthcare and Medicine
An AR scanner is a powerful tool for most areas of healthcare. AR is a strong match for multiple specialized usage scenarios. For example, surgeons can see organized visualizations during an operation. Augmented reality recognition tools can also be of tremendous medical value for more generalized use. Healthcare workers can use AR to instantly see a patient’s vitals, anatomical markers or status, and pre-operative or post-operative imagery. The hands-free nature of AR data makes it easy to integrate into existing medical workflows. Institutions like the Imperial College of Healthcare NHS Trust in London are even using AR headsets to see CT scans during reconstructive surgery. If you want to learn more about the applications of AR in healthcare industry, read “Augmented Reality in Healthcare; Clear Examples of AR in Healthcare.”
3. Education and Training
Students using AR scanner technologies can experience subjects through immersive technology. Previously, static images in textbooks were transformed through animation, video, and even 3D representations. Likewise, normally difficult or even dangerous training can be enhanced and safeguarded through AR. Applying AR to education has led to some impressive results. For example, students at Saddleback College are using Pearson Education’s AR app with textbooks and have increased their comprehension rate by 70%. If you want to learn more about how AR is transforming education, read “The Role of Augmented Reality in Modern Classrooms.”
5. Manufacturing and Maintenance
Industrial settings are inherently complex environments. As such, AR’s ability to display and organize data in a hands-free, step-by-step manner can offer significant advantages for most projects. AR detection tools can observe a changing environment and guide workers through multilayered assembly processes. Simply pointing an AR scanner at a part might identify it while also displaying diagnostic information in real-time. This also helps minimize performance gaps between newer workers and those with more experience. AR has been shown to extend equipment’s life while also minimizing downtime. An impressive example of this concept can be seen with Porsche’s “Tech Live Look” system. Technicians simply need to scan parts of an engine to receive information and remote, expert guidance in real-time. This has resulted in a 40% reduction in service time.
Video: Tesla Cybertruck Toy: 3D Scan with AR Code Object Capture
5. Architecture and Construction
AR has had a significant impact on many areas within construction and architecture. Project managers working in construction can use augmented reality scanner technologies to see the completed project layered on top of the in-progress construction site. Construction workers can use AR to essentially look into walls and see plumbing, wiring, structural points, and other elements that would require additional consideration. Clients also benefit by seeing non-technical, visual representations of proposals and projected results. This increases satisfaction while decreasing the need for revision – translating into cost reduction. Trimble’s SiteVision, for example, is used by the McCarthy Building Companies. In doing so, they reduced the rework costs of advanced healthcare facility construction by 30%.
Top AR Scanner Apps in 2025
The augmented reality scanner ecosystem and its implementations are growing at a rapid pace. The following are some of the best, most powerful AR scanner apps.
1. AR Scanner
AR Scanner is a popular option for people in marketing, education, and retail as it can turn static images into an immersive experience. Users simply scan AR markers on an object and watch as interactive controls, 3D models, video, and more suddenly spring to life. The system is quite flexible and easy to use with posters, packaging, boxes, and brochures. The easy-to-use nature of the system makes it ideal for both creators and end users alike.
2. ScanAR – The Augmented Reality
ScanAR is a powerful tool for anyone working in publishing, marketing, or hosting events. Users simply point the augmented reality scanner at printed material and watch as it becomes an interactive experience. Some examples include business cards, flyers, or any printed material used to communicate with potential customers and clients. While no coding experience is required, it still provides advanced functionality, like the use of cloud-based technologies for performance metric tracking. The system provides an easy way to transition from older methods of marketing into a more modern form of storytelling that appeals to a new audience. At the same time, the existing methods can still be used alongside it depending on the end user’s personal preferences. It’s an ideal way to build brand identity and engagement within new and existing markets.
3. ARLOOPA
ARLOOPA is an incredibly flexible and user-friendly AR app that makes it easy to add digital elements to any real-world environment. The system’s AR scanner supports both markerless and marker-based use. A combination of a huge library and a user-friendly interface has made it a hit in e-commerce, entertainment, and education. It’s easy to use the app to scan markers, which will bring a 3D experience to life with enchanting digital models. The system also makes it easy to create your own custom content. The app can leverage spatial audio, video, and many types of animation, which creates a truly immersive multimedia experience. It’s also easy to share the experience with friends thanks to its dual support of both Android and iOS.
Video: ARloopa – How to Use Scanner – Tutorial
4. AR Code Object Capture 3D Scan
AR Code Object Capture 3D Scan uses photogrammetry to move beyond the standard marker-based systems used in most AR apps. Users leverage the augmented reality scanner to convert physical objects into an AR-based model. The scanned 3D model can then be used for a wide variety of other applications and solutions. It’s proven to be especially popular among retailers, designers, educators, and anyone who wants to display 3D elements within physical environments. The system also opens up deployment options through its AR Code platform, which converts the new assets into WebAR experiences. The sheer realism of the models has made it an appealing option for companies who want to entice and engage customers with an expansive selection of notable items. The system’s utility is further enhanced by how well it can scale to different needs.
Video: Museum Augmented Reality with AR QR Code & 3D Scanning
5. Scandit Barcode Scanner
Scandit Barcode Scanner differs in some significant ways from the standard AR scanner. It’s heavily tied into barcodes and is one of the leading apps for those usage scenarios. Users simply need to scan a barcode, and they’ll quickly see tailored information through an AR display. The details shown and how it’s used will, of course, vary by sector. The Scandit Barcode Scanner system has displayed exceptional popularity within healthcare, logistics, and retail. This is due in part to the system’s powerful operational efficiency. Many apps struggle with damaged barcodes or only support a subset of the various formats. However, Scandit Barcode Scanner will often even work with damaged labels in areas with poor lighting. There’s no need for manual data entry or special attention to the labels. Users can simply scan and trust.

6. ROAR Augmented Reality App
The ROAR Augmented Reality App is specially tailored to the needs of AR marketing campaigns. Companies and individuals alike will find a wide variety of powerful options for both markerless and marker-based augmented reality campaigns. On the user side, people simply need to use an image with the augmented reality scanner. This process turns the standard, static marketing information into a dynamic and immersive experience tailored to a specific goal or subject.
The experience can vary from 3D models to animated marketing, product demos, and more. On the creator side, the system makes it easy to create and track campaigns through a drag-and-drop interface and analytic tools. These tools also help bolster the analysis of ROI and user interactions. The system’s WebAR support means that even people just using their web browser rather than an app can get the full experience. The ROAR Augmented Reality App has received considerable attention in education, publishing, and retail.
7. Halo AR – 3D Creator & Scanner
Halo AR – 3D Creator & Scanner is an easy-to-use system that’s an ideal match for educators. The system doesn’t require any coding experience to use. Instead, users can create or activate AR experiences through an intuitive interface that supports 3D models, video, text, web links, and more. Any field that needs a powerful solution for creative storytelling, which melds text and immersive technology, will quickly find potential within the app. It’s so easy to use that AR experiences can be designed right from your phone. Likewise, you can access its creations through web browsers that support WebAR.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality Scanners
AR scanner technologies are evolving at a rapid pace. Each of the following technologies is providing new innovations to expand AR’s already impressive potential.
- AI Integration: AR and AI are converging as augmented reality scanner technologies integrate machine learning for context awareness, predictive algorithms, advanced image recognition, and more.
- Wearable AR Devices: Hands-free applications are seeing some major upgrades thanks to AR scanner integration into headsets and smart glasses in order to aid in healthcare, field service, manufacturing, and more.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing can bypass the cloud to perform operations in real-time with low latency in order to enhance the capabilities of applications that need instant responses.
- Cloud AR: Meanwhile, the cloud lets AR scanner technologies stay up-to-date, process more difficult levels of data, provide complex visualizations, and all with low battery use.
- Spatial Anchoring: Persistent spatial positioning allows for precise placement of digital elements in physical spaces, ideal for both industrial use and multi-user experiences.
- Democratized Development: Companies without specialized backgrounds in AR will use new tools to leverage augmented reality scanner technologies, vastly increasing AR adoption and development.
Augmented Reality Printing: How to Bring Static Content to Life?
Augmented reality printing leverages augmented reality image scanners to bring magazines, papers, packages, marketing, and any static image to life. The technique seamlessly bridges traditional media with new immersive technologies. You can learn the basics of AR printing, how it shapes the public’s reactions, and methods to integrate it into a business plan in the article “Augmented Reality Printing: How to Bring Static Content to Life?”
Augmented Reality Builder Options; Building Your Digital Dreams
Augmented reality builders are systems used to create AR apps, content, and experiences. Many AR builders provide intuitive interfaces that don’t require much, if any, coding experience thanks to drag-and-drop methodology and pre-built templates. These systems open up AR design to teachers, businesses, and all types of creators. You can discover the best AR builder systems and their most important elements, guides to your first projects, and more in the article “Augmented Reality Builder Options; Building Your Digital Dreams”.
FAQs About Augmented Reality Scanners
What is the Difference Between AR Scanners and Traditional Cameras?
AR scanners combine cameras with specialized software and sensors to recognize objects and overlay digital information. In contrast, traditional cameras only capture images without interactive digital enhancement.
Do I Need Special Hardware to Use AR Scanners?
Most AR scanner apps work with standard smartphones and tablets. Advanced applications may require specialized devices like smart glasses or dedicated AR hardware.
How Accurate are AR Scanners for Professional Use?
Professional AR scanners like AccuVein achieve 97.4% accuracy in medical applications, while industrial scanners can reduce errors by up to 38% compared to traditional methods.
Can AR Scanners Work Offline?
Basic AR functionality works offline, but many features, like real-time data overlay and cloud-based content, require internet connectivity.
What Industries Benefit Most from AR Scanner Technology?
Healthcare, retail, education, manufacturing, and construction see the greatest benefits, with measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and user engagement.
Augmented reality scanner technologies are changing how people in most sectors interact with information. AR enhances understanding by creating immersive, engaging experiences from otherwise static information. You can explore the options and get ahead of the competition by considering everything you’ve learned here.
Did You Like This Article About AR Scanners?
You might also be interested in the following articles:
- How Augmented Reality Entertainment is Transforming Media
- Best AR Games: Top Augmented Reality Games to Play
- Best AR Workshops to Boost Learning Through Immersive Tech







Leave A Comment